The Productivity Revolution: How Automation Is Transforming Work

The modern workplace is rapidly adopting automation. This isn't about robots replacing humans, but about strategically integrating technology to optimize operations and empower employees. This shift represents a fundamental change in how we work, enabling us to redirect human talent towards more strategic, higher-value tasks and achieve significant productivity gains.
Unlocking Efficiency and Empowering Employees
The primary benefit of automating repetitive tasks is the liberation of human capital. Consider the substantial amount of time typically spent on data entry, email filtering, or report generation. These are necessary tasks, but they can often be tedious and drain employees' energy and creativity. Automation allows businesses to delegate these routines, freeing up employees to focus on strategic initiatives, complex problem-solving, and driving innovation.
For example, imagine a marketing team dedicating hours each week to compiling campaign performance reports. By automating data collection and report generation using tools like Google Analytics, marketers can dedicate more time to analyzing results and crafting more impactful campaigns. This shift directly improves productivity and contributes to better business outcomes. Moreover, it fosters a more engaged and satisfied workforce.
Automating repetitive tasks has become essential for productivity in today's workplaces. By automating routine processes, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and increase employee satisfaction. For example, automation has improved the jobs of 90% of knowledge workers and boosted productivity for 66% of them, showcasing a considerable positive impact. According to McKinsey, roughly 50% of work activities have the potential for automation, highlighting vast opportunities for efficiency gains.
This trend indicates that while automation can replace some tasks, it is primarily leveraged to optimize specific processes, not entire roles. Less than 5% of jobs are fully automatable. As a result, automation helps employees focus on more creative and high-impact work by reducing the burden of repetitive tasks like data entry and email management. For more in-depth statistics on automation, visit Kissflow.
The Ripple Effect of Automation
The benefits of automating repetitive tasks extend far beyond individual employees. It generates a ripple effect across entire organizations, leading to improved efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced overall performance. When processes are streamlined and standardized, the likelihood of human error decreases significantly. This results in higher-quality outputs, less rework, and ultimately, increased profitability.
Furthermore, automation enables businesses to scale more effectively. As a company grows, the volume of repetitive tasks can quickly become overwhelming. Automation offers a scalable solution, enabling businesses to manage increasing workloads without a proportional increase in staff. This helps companies maintain agility and responsiveness in a dynamic business environment. The enhanced efficiency directly translates into cost savings and faster time to market. Ultimately, automating repetitive tasks paves the way for a more innovative, efficient, and human-centric workplace.
Finding Your Automation Gold Mines: Tasks Worth Transforming
Not all repetitive tasks offer the same benefits when automated. Some yield significant returns, while others may not justify the effort. Identifying these "automation gold mines" requires a thorough analysis of your current workflows. This involves working with team members who understand the processes to pinpoint hidden inefficiencies. These inefficiencies often reveal ideal candidates for automation. This section provides a practical framework for pinpointing those tasks that consume valuable time without delivering corresponding value.
Identifying Automation Opportunities
The first step is workflow mapping. This involves documenting each step of a process, from beginning to end. This visual representation clarifies dependencies, bottlenecks, and areas ripe for automation. For instance, a marketing team could map their social media posting process, highlighting the time spent manually scheduling posts. This can reveal the potential benefits of automating this task.
Consider using techniques like time tracking and process mining to quantify the actual time spent on repetitive tasks. This data provides a concrete basis for calculating potential time savings. This concrete data also helps to build a strong business case for automation. Tools like AI Notetaker can be valuable assets in documenting workflows and tracking time.
To better illustrate common repetitive tasks across different departments, let's examine the following table:
Common Repetitive Tasks Across Departments
| Department | Repetitive Task | Est. Weekly Hours Spent | Automation Difficulty | Potential Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | Social Media Posting | 5 | Low | 4 |
| Sales | Lead Qualification | 10 | Medium | 6 |
| Customer Service | Responding to FAQs | 15 | Low | 10 |
| Human Resources | Onboarding Paperwork | 8 | Medium | 5 |
| Finance | Invoice Processing | 12 | High | 8 |
This table identifies routine tasks in different business departments that are prime candidates for automation, including the estimated time savings and difficulty of implementation. As the table shows, departments like Customer Service and Finance spend a considerable amount of time on tasks that could be automated.
Prioritizing Automation for Maximum Impact
After identifying potential automation targets, the next step is prioritization. Not every task needs immediate automation. Focus on those with the highest potential Return on Investment (ROI). These include tasks that are:
- High-frequency: Performed regularly, leading to substantial cumulative time savings.
- Error-prone: Automation reduces human error, improving accuracy and minimizing rework.
- Time-consuming: Freeing up employee time for more strategic activities.
- Easily standardized: Processes with clear, consistent steps are simpler to automate.
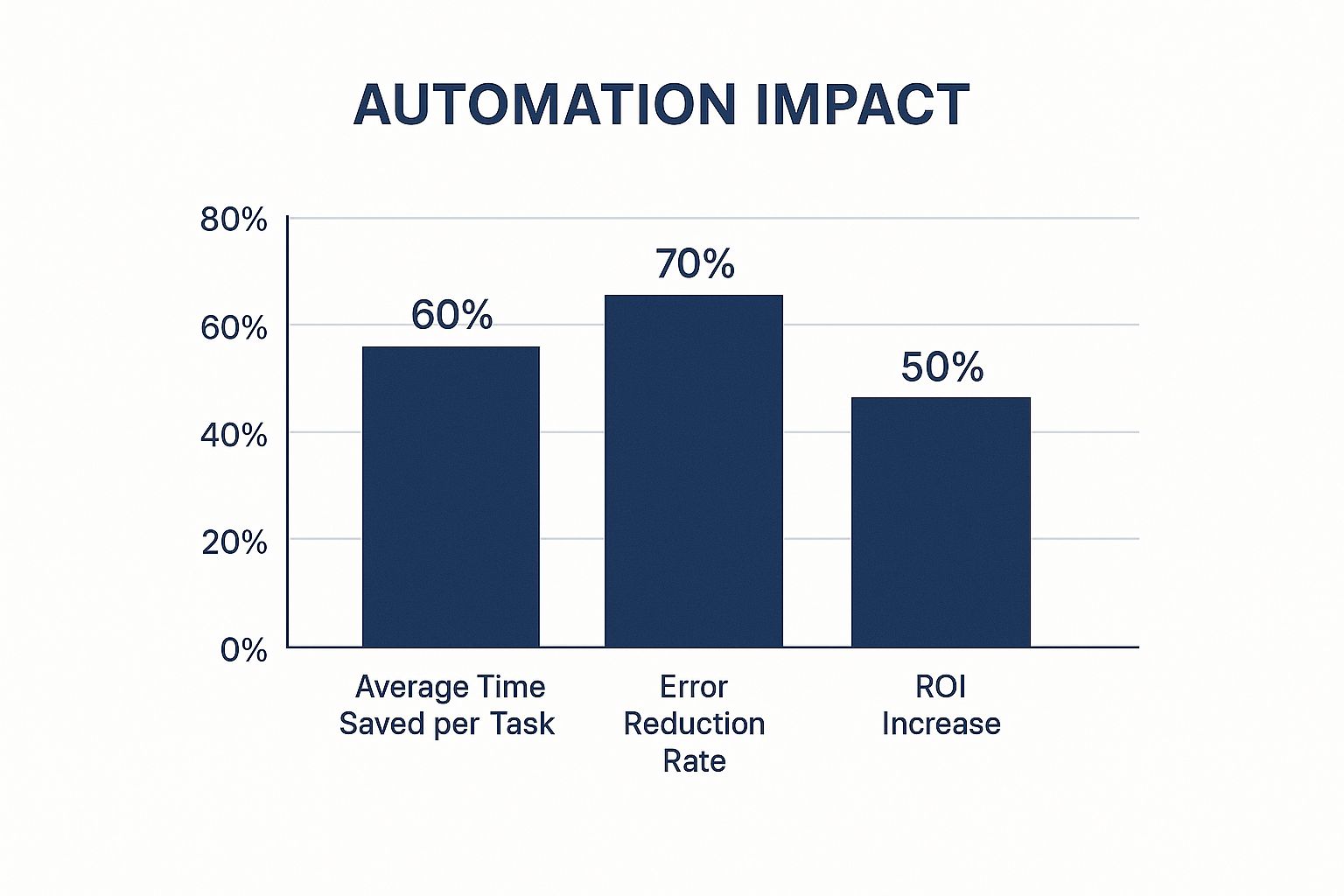
The infographic above visualizes automation's potential impact on three key metrics: time saved, error reduction, and ROI increase. Automating repetitive tasks can lead to a 60% reduction in time spent per task, a 70% decrease in errors, and a 50% increase in ROI. These benefits highlight automation’s transformative power. Studies show over 40% of workers spend at least 25% of their time on tasks like data collection and email management. Automation can reclaim a significant portion of this time, with nearly 69% of workers believing it can lessen their workload. Furthermore, 66% note automation's ability to minimize human error, allowing employees to reclaim up to 59% of their time for more meaningful work. The fact that 94% of companies perform repetitive tasks further emphasizes the potential of automation. For further insights into automation, explore this resource: Automation of Repetitive Tasks.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Implementing automation can sometimes meet resistance from team members used to traditional workflows. Addressing these concerns requires open communication and demonstrating automation's benefits for both the individual and the organization. This includes showing how automation creates opportunities for more engaging work, rather than eliminating jobs. By emphasizing the positive impact on career development and job satisfaction, you can foster a culture that embraces automation as a tool for growth. This shift in perspective is critical for long-term success.
Your Automation Toolkit: Selecting The Right Solutions

With the wide variety of automation tools available, choosing the right one can be a daunting task. This section offers practical guidance for navigating the world of automation, focusing on matching solutions to your specific needs, understanding integration options, and considering the learning curve for your team. Effective automation relies on choosing the right tools for the job, just like selecting the right tool from a toolbox. A hammer isn't designed for tightening screws, and similarly, a basic scripting tool won't be effective for automating complex enterprise workflows.
Categories Of Automation Tools
Automation tools can be broadly classified based on their complexity and purpose:
-
No-Code/Low-Code Platforms: These tools enable automation through visual interfaces and pre-built modules, requiring minimal coding. They're ideal for simple, repetitive tasks like data entry or social media posting. Think of them as the versatile screwdriver in your automation toolkit.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA tools emulate human actions to automate tasks involving multiple applications. They're well-suited for complex workflows like invoice processing or managing customer data across different systems, much like a power drill handles demanding tasks.
-
Business Process Management (BPM) Software: BPM tools optimize entire business processes end-to-end, often incorporating both RPA and other automation technologies. This is akin to having a fully equipped workshop at your disposal.
-
Specialized Automation Tools: These tools are designed for specific functions like marketing automation, IT automation, or design automation. Design automation, for instance, can significantly streamline the design process, especially for customized products. For more information on another type of automation, see our article about the benefits of static code analysis. These are like specialized tools in your toolkit, perfect for specific situations.
To help you choose the right automation tool for your needs, we've compiled a comparison table highlighting the key features, pricing, and implementation considerations of several leading platforms.
The table below, "Automation Tool Comparison," provides a detailed comparison of leading automation platforms. We've examined key features, typical pricing, ease of implementation, and integration capabilities to help you select the best fit for your requirements.
| Tool Name | Best For | Key Features | Price Range | Ease of Implementation | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiPath | Enterprise-grade RPA | AI-powered automation, robust integration, attended and unattended robots | $$ | Moderate | Extensive |
| Automation Anywhere | Intelligent Automation | Cloud-native, cognitive automation, process discovery | $$ | Moderate | Extensive |
| Kissflow | Low-code BPM | Workflow automation, case management, collaboration tools | $ | Easy | Moderate |
| Zapier | No-code automation | Connecting apps and automating workflows, simple interface | $ | Easy | Wide range of web apps |
| Make (formerly Integromat) | Advanced no-code/low-code | Visual workflow builder, complex scenarios, API integration | $ | Moderate | Extensive API integrations |
This table summarizes some of the leading automation platforms and their strengths. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and resources.
Evaluating Automation Solutions
When choosing an automation tool, consider these key factors:
-
Ease of Use: How quickly can your team learn and use the tool? No-code platforms are generally easier to use than RPA or BPM solutions.
-
Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with your existing systems is crucial for data flow and prevents data silos.
-
Scalability: Can the tool handle growing workloads and increasing complexity as your automation needs evolve?
-
Cost: Consider both upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Negotiating pricing and getting internal buy-in are important steps.
-
Vendor Support: Adequate training, documentation, and technical support from the vendor are essential.
Building Your Automation Roadmap
Automating repetitive tasks should be a strategic initiative, not a one-time project. Start by identifying your automation goals and prioritizing tasks with the highest return on investment (ROI). Select the tools that best meet your needs and create a phased implementation plan. Begin with smaller pilot projects to test and gather feedback before expanding.
A successful automation strategy requires continuous improvement and adaptation. As your needs change, you may need to re-evaluate your tools and incorporate new solutions. This ensures your automation efforts stay effective and aligned with your business objectives. This iterative approach allows for flexibility and minimizes disruption.
From Concept to Reality: Implementing Automation That Works
The immense potential of automation is often talked about, but realizing that potential requires careful planning and execution. Bridging the gap between identifying automation opportunities and successfully implementing solutions can be a challenge for many organizations. This section offers a practical roadmap, drawing from the experiences of automation project leaders, to transform promising concepts into effective automated systems.
Building a Foundation for Success
Implementing successful automation begins with securing stakeholder support. Buy-in is crucial, and it's achieved by clearly communicating the benefits of automation, addressing any potential concerns, and involving stakeholders in the planning process. This includes acknowledging fears about job displacement and emphasizing how automation can create new opportunities for employees to focus on more strategic and fulfilling work. For managing workflows, consider tools like those used for Automating Jira HubSpot Workflows.
Effectively documenting existing processes is another vital step. This helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, providing a clear baseline to measure the impact of automation. This documentation also serves as a valuable guide during implementation. Resources like How to master code structure best practices can be helpful. This understanding lays a strong foundation for a successful automation journey.
Piloting Your Automation Project
Choosing the right pilot project is key to building momentum. Begin with a well-defined, manageable project with a high probability of success. This early win can showcase the tangible benefits of automation and encourage wider adoption across the organization. A successful pilot acts as a catalyst for future automation initiatives.
Building cross-functional implementation teams is also essential. These teams should combine technical expertise with business understanding and include representatives from the departments impacted by the automation, ensuring alignment and collaboration. This cross-functional approach helps navigate implementation complexities.
Navigating the People Side of Automation
Successful automation isn't solely about technology; it's about people too. Addressing concerns about job displacement, providing training opportunities, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are vital for long-term success. This involves open communication, transparent processes, and a commitment to employee development.
Establish meaningful success metrics to track progress and demonstrate automation's value. These metrics should align with business goals and measure not just time savings, but also improvements in accuracy, quality, and customer satisfaction. This data-driven approach helps justify continued investment in automation.
Overcoming Technical Hurdles
Technical challenges can often derail automation projects. Careful tool selection, thorough testing, and robust change management processes are essential to avoid common pitfalls. This includes ensuring tools integrate with existing systems and providing ongoing user support. A proactive approach to technical issues minimizes disruptions and maximizes success.
Realistic timelines and resource planning are also crucial. Automation projects vary in complexity and scope, so setting realistic implementation expectations and allocating resources accordingly is essential. This includes budgeting for software, hardware, training, and support. Proper resource allocation ensures a smoother implementation process. Following these principles allows organizations to move from the theoretical potential of automation to the practical reality of improved efficiency, increased productivity, and a more engaged workforce.
The Human Element: Thriving in an Automated Workplace

As businesses increasingly adopt automation for repetitive tasks, a vital question arises: how can we flourish in this changing work environment? The answer lies not just in implementing new technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), but also in redefining the human role. This involves adapting roles, acquiring new skills, and building a culture that supports human-machine collaboration.
The Changing Landscape of Skills
Automation significantly impacts the job market, presenting both obstacles and new possibilities. The widespread adoption of automation has far-reaching implications for the global workforce. Currently, 2.5 million industrial robots operate worldwide, showcasing automation's significant presence in industries like manufacturing.
By 2030, 46.5% of jobs in North American energy, utilities, and mining are projected to be at high risk of automation. While this may lead to job displacement, it also creates opportunities for increased efficiency and upskilling. For example, by the end of 2024, an estimated 69% of managerial tasks are predicted to be automatable, emphasizing the need for managers to evolve.
Since 1980, AI and automation have contributed to wage reductions of up to 70% in some sectors. However, the overall trend suggests automation focuses on optimizing tasks rather than complete job replacement. Learn more about the impact on employment with these job displacement and automation statistics. This shift demands a proactive approach to workforce development, focusing on skills that complement automated systems.
Upskilling for the Future
Forward-thinking companies are investing in upskilling and reskilling programs to equip employees for the demands of an automated workplace. This involves cultivating uniquely human skills that are difficult for machines to replicate:
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: Analyzing complex situations, identifying solutions, and making sound decisions.
- Creativity and Innovation: Developing new ideas, innovative approaches, and adapting to unexpected challenges.
- Emotional Intelligence and Empathy: Understanding and responding to others' emotions, building relationships, and fostering collaboration.
- Communication and Collaboration: Conveying information effectively, working in teams, and achieving consensus.
These skills become even more crucial as automation handles routine tasks, freeing up humans for higher-level responsibilities. This shift also requires a change in mindset, encouraging employees to view automation as an opportunity for professional growth.
Redesigning Roles for Human-Machine Collaboration
To fully realize human potential in an automated workplace, organizations must redesign roles to leverage human strengths. This involves creating new job categories that blend human expertise with the capabilities of automated systems. For instance, instead of manual data processing, employees might focus on interpreting data insights generated by AI algorithms. You can explore further on how roles are evolving in the face of technological advancement by reading about how to manage the challenges of monorepos, which often arise in collaborative, tech-driven environments.
Cultivating Collaborative Intelligence
This approach fosters collaborative intelligence, where humans and machines work together, leveraging their respective strengths. Machines excel at processing large datasets and performing repetitive tasks accurately, while humans provide creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence. This synergy leads to a more efficient, productive, and fulfilling work environment. By embracing collaboration, organizations can unlock new levels of innovation and achieve sustainable growth in the age of automation. Adapting to this changing landscape requires a proactive and strategic approach to workforce development, fostering a culture of continuous learning and embracing the opportunities that automation offers.
Measuring What Matters: Proving Automation's True Value
Automating repetitive tasks offers more than just time savings; it represents a strategic investment in efficiency and productivity. But how can you accurately measure the full impact of this investment and justify continued spending on automation initiatives? This section provides a framework for quantifying both the obvious and less apparent returns from automation, enabling you to build a compelling case for its continued adoption.
Establishing Meaningful Baselines
Before implementing any automation, it's crucial to establish clear baselines for the metrics you aim to improve. This provides a foundation for accurately measuring the impact of your automation efforts. For instance, if you're automating customer service responses, track metrics like average handling time, resolution time, and customer satisfaction scores before implementing the automation. This establishes a benchmark for comparing post-automation performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Automation
Tracking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for demonstrating automation's value. While these will vary depending on the specific processes being automated, some common KPIs include:
- Time Savings: Measure the reduction in time spent on tasks after automation is implemented. This directly reflects increased efficiency.
- Error Reduction: Track the decrease in errors or defects as a result of automation. This highlights improvements in quality and accuracy.
- Productivity Gains: Quantify the increase in output or completed tasks per employee post-automation, demonstrating enhanced efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Calculate the reduction in labor costs, material waste, or other expenses due to automation. This reveals the financial benefits.
- Employee Satisfaction: Gauge how automation impacts employee morale and job satisfaction, capturing the human aspect of these changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Monitor changes in customer satisfaction scores after automating customer-facing processes, reflecting improvements in customer experience.
As an example, a company automating invoice processing might track KPIs such as the number of invoices processed per hour and the error rate in invoice data entry. This data offers concrete evidence of the automation's impact.
Communicating Automation Wins
Effectively communicating the benefits of automation to leadership is critical for securing continued investment. Present your findings using clear visuals, like charts and graphs, that highlight the key improvements. Focus on how automation impacts overall business objectives, such as increased revenue, reduced costs, or improved customer satisfaction. A compelling Return on Investment (ROI) analysis demonstrating the financial benefits of automation is particularly effective.
Unveiling Hidden Benefits
Beyond readily quantifiable benefits, automation often yields significant, less obvious advantages. These are often harder to measure but equally valuable. They include:
- Reduced Employee Burnout: Automating tedious tasks frees employees from repetitive work, leading to reduced stress and burnout, potentially improving employee retention and productivity.
- Increased Innovation Capacity: By freeing up employee time, automation allows them to focus on more creative and strategic endeavors, fostering innovation.
- Improved Employee Engagement: Employees engaged in more challenging and meaningful work tend to be more motivated and productive. Automation can facilitate this shift by reducing the burden of routine tasks.
- Enhanced Scalability: Automation allows businesses to handle increasing workloads without a proportional increase in staff, enabling efficient scaling as the business grows.
While these benefits may be challenging to quantify directly, consider using qualitative data like employee surveys or feedback sessions to capture their impact. This provides a more holistic view of automation's true value.
Building a Compelling ROI Analysis
A robust ROI analysis is crucial for justifying continued investment in automation. Utilize the data collected to quantify the financial benefits, including cost savings, revenue increases, and improved profitability. Compare these benefits to the costs of implementing and maintaining the automation to present a clear picture of the ROI. This data-driven approach demonstrates the value of automation and secures ongoing support for your initiatives. By measuring what truly matters and effectively communicating the value of automation, you can build a strong case for continued investment and ensure long-term success.
Beyond the Basics: Creating a Sustainable Automation Culture
The true potential of automating repetitive tasks isn't realized through one-off projects. Instead, it's about fostering a culture that embraces automation as a continuous improvement strategy. This requires a shift in mindset, viewing automation not as a job eliminator, but as a powerful tool for empowering employees and driving business growth. Let's explore how leading organizations build this sustainable automation culture.
Establishing an Automation Governance Framework
A robust governance framework is crucial for managing automation initiatives effectively. This framework should define clear roles and responsibilities, establish standardized processes for development and deployment, and ensure compliance with security and regulatory requirements. For instance, a clear approval process for new automation projects ensures alignment with business objectives and prevents the uncontrolled spread of automation tools.
Maintaining and Updating Automation Assets
Automation isn't a "set it and forget it" solution. Like any software, automation tools and processes require regular maintenance and updates. This includes monitoring performance, fixing bugs, and adapting to evolving business needs. Creating a dedicated team or assigning responsibilities for automation maintenance ensures these assets remain effective and deliver consistent value. This ongoing effort is critical for realizing the long-term benefits of automation.
Fostering Cross-Functional Collaboration
Identifying new automation opportunities requires collaboration. Creating cross-functional teams with representatives from different departments allows for shared insights into respective workflows. These teams can identify common pain points and brainstorm potential automation solutions. This collaborative approach breaks down silos and fosters a shared understanding of automation’s potential across the organization.
Embracing a Culture of Continuous Improvement
A sustainable automation culture requires a mindset of continuous improvement. Encourage employees to identify new automation opportunities and provide feedback on existing processes. Invest in training programs to develop automation skills. By viewing automation as an ongoing journey of learning and adaptation, organizations can ensure their initiatives remain effective and align with evolving business objectives.
Adapting to Emerging Technologies
The field of automation is constantly evolving. New technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) create new possibilities for automating complex tasks. Organizations need to stay informed about these emerging technologies and explore how to incorporate them into their automation strategies. This forward-thinking approach ensures they can fully leverage advancements and maintain a competitive edge.
Ready to flatten your repositories and prompt faster? Streamline your code preparation with TreeSnap. Our platform simplifies complex codebases, allowing you to focus on what matters most – building innovative solutions.